Chronic Kidney Disorder (CKD) is a chronic medical condition characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function. It affects millions of individuals worldwide, making early detection and intervention paramount. The kidneys’ vital role in filtering waste products from the blood makes CKD a severe health concern.
The Challenges
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) often goes unnoticed in its early stages, highlighting the need for regular check-ups, especially for those with risk factors.
Common tests like Complete Blood Count, Urinalysis, and Blood tests are crucial for early CKD detection.
PredictEasy’s User-Friendly Model simplifies CKD risk assessment based on specific factors, making it accessible for individuals of varying ages and medical histories.
Data Integration Challenges: Integrating diverse medical data seamlessly into the system requires compatibility across various test formats and data sources.
User-Friendly Interfaces: Ensuring user-friendly interfaces for individuals with different technical skills is crucial for accessibility and efficiency.
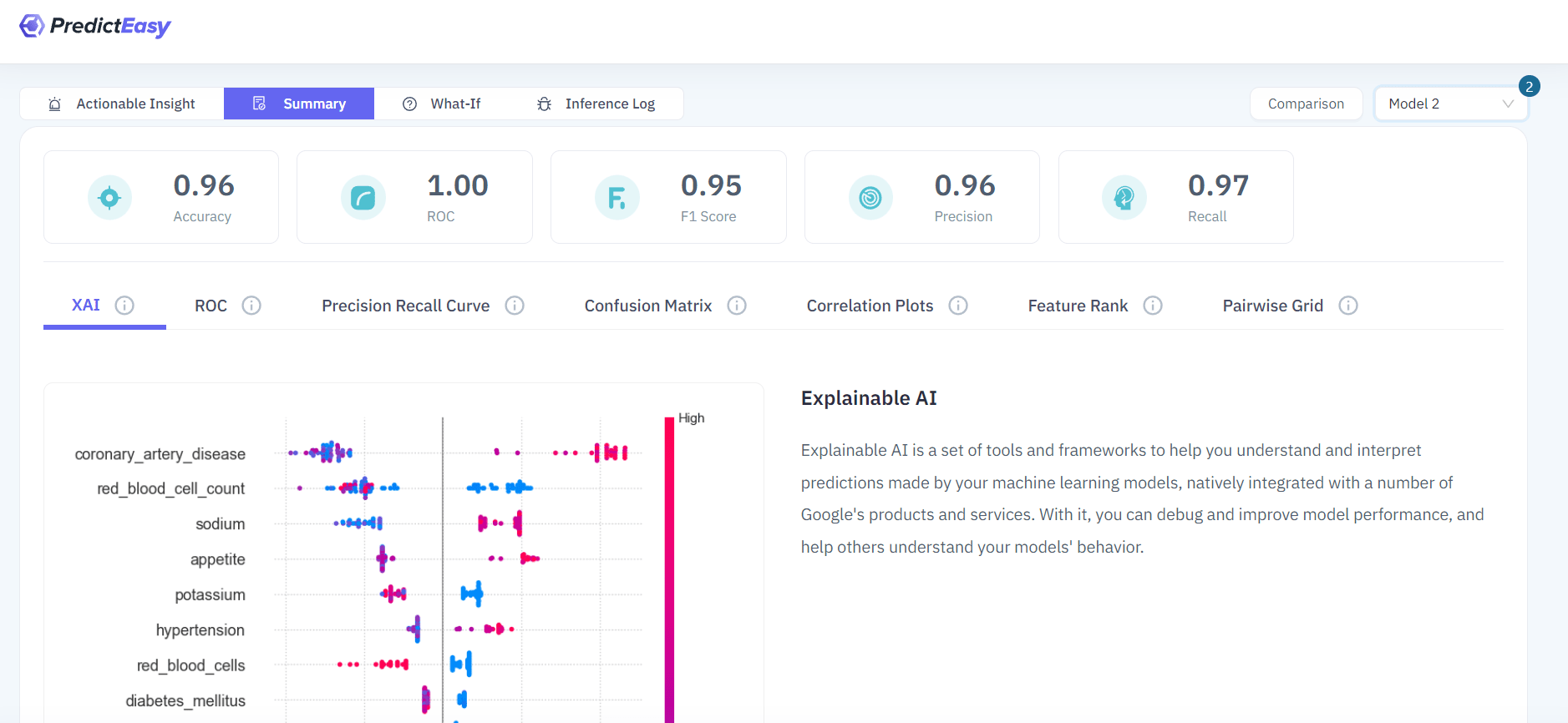
Accuracy and Result Interpretation: Achieving high accuracy in predictive models and ensuring clear result interpretation are ongoing challenges, emphasizing the importance of transparent explanations.
What did PredictEasy do
Used for creating machine learning models for chronic kidney disease (CKD) data.
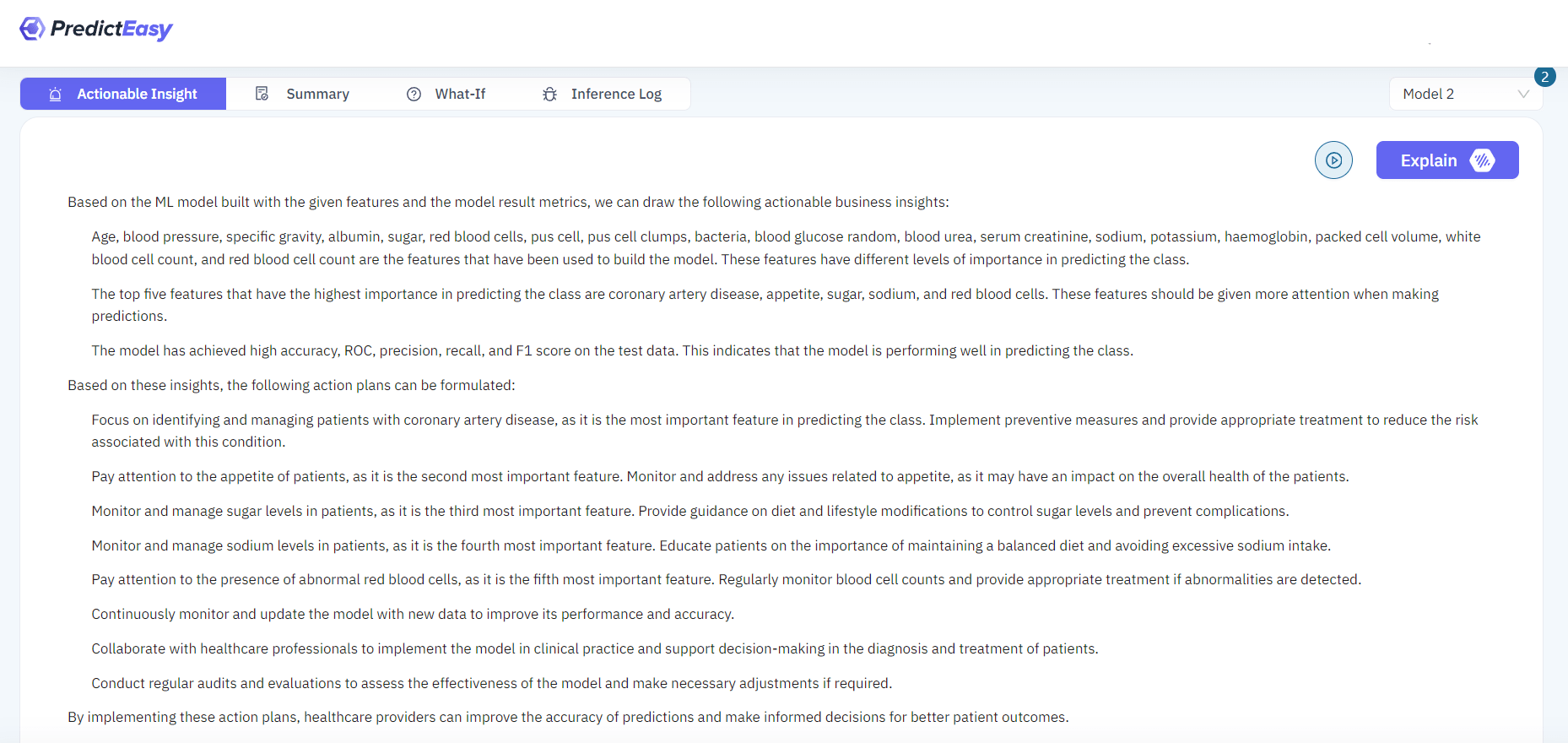
Provides Performance Metrics, SHAP value chart, Feature Importance, and a tool for exploring “What if” scenarios.
Dynamic real-time interface for modifying model inputs and observing resulting outputs. Offers predictions, confidence levels, and detailed explanations for the adjustments made.
Develops an accessible and effective predictive model for assessing CKD risk. Simplifies the process of evaluating an individual’s probability of developing CKD.
Users can easily determine their susceptibility to CKD by inputting specific medical test results into the PredictEasy model.

The Results
CKD Probability Comparison:
Using What-If Simulator, a 45-year-old patient with identical test results as a 30-year-old has a 52% probability of developing CKD, while the younger patient has a 34% chance. Age plays a crucial role in CKD risk assessment.
Impact of Sodium Levels:
Excessive sodium can lead to water retention, causing swelling, high blood pressure, and potential kidney damage. Maintaining sodium levels between 135 and 145 mEq/L is crucial for kidney health.
Potassium and Kidney Health:
Elevated potassium levels, especially in individuals with damaged kidneys, can be life-threatening, affecting the heart's rhythm. Keeping potassium levels between 3.5 and 5.2 mEq/L is essential for kidney patients.
Factors Influencing CKD:
High blood sugar, hypertension, and a family history of diabetes significantly contribute to CKD. Diabetes, driven by prolonged high blood sugar and elevated blood pressure, is the leading cause of CKD, eventually leading to kidney failure. Holistic health management is crucial for predicting and preventing CKD.